China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is an economic corridor which is under development and partially completed aimed to fully facilitate trade route that connects Pakistan (Gwadar) and China (Kashgar) through the development and construction of railways, highways and pipelines, energy sectors and development of Gwadar port worth nearly $64 billion.

China Pakistan Economic Corridor is a structure and framework of regional connectivity of Pakistan with China. China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is a massive bilateral project to improve the infrastructure within Pakistan to put the trade on the fast track with China and it will be further integrated with other countries of the region. CPEC is not only supposed to benefit Pakistan or China but will have a positive impact on Asian states like; Afghanistan, Iran, India and Central Asian Republic states and the entire region. China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) was launched on April 20, 2015, by Pakistani Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif and Chinese President Xi-Jinping and signed MOU of 51 agreements with the total worth of $64 billion. The objective of CPEC is to
Transform Pakistan Economy by modernizing, developing and upgrading its Roads, Railway System, Air transport system and Energy sectors for industries.
Connectivity of deep sea ports of Gwadar and Karachi to China’s province Xinjiang as well Asia, Europe and Africa. The border of Xinjiang connects the countries of Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and India. These are connected with ancient silk road.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor offers free and frequent exchanges of people to people contact and exchange of businesses, exchange and understanding of academic, cultural and regional knowledge and activity of high volume trades and production of energy from the energy sectors. China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is the part of larger Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) which is focused to improve the Connectivity of regions, Communication, trade and cooperation between the countries of Europe-Asia. China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is an objective and destination towards economic regionalization in the global world. It offers development, peace and win-win model for all.
The Chinese government has a significant strategic interest in Gwadar Port. In 2013, China Overseas Ports Holdings Company Limited (COPHC) took control of the port, recognizing its crucial role in China’s global trade and energy security.
Why is Gwadar Port Important for China?
China relies heavily on Persian Gulf oil, with about 60% of its oil trade passing through the Strait of Malacca, covering nearly 16,000 kilometers in one to two months. This route exposes China to bad weather, political conflicts, and security risks, particularly at its only commercial port, Shanghai.
Gwadar Port provides China with a shorter and safer route, cutting 5,000 kilometers from the traditional shipping path and ensuring year-round operations.

The Pakistani government has proposed a naval base for China at Gwadar, strengthening bilateral relations. However, analysts suggest that while China has shown interest, it remains cautious due to potential geopolitical reactions from India and the USA.
Gwadar is a key part of CPEC, which extends beyond infrastructure to include:
✅ Road and railway development
✅ Energy projects
✅ Agricultural initiatives
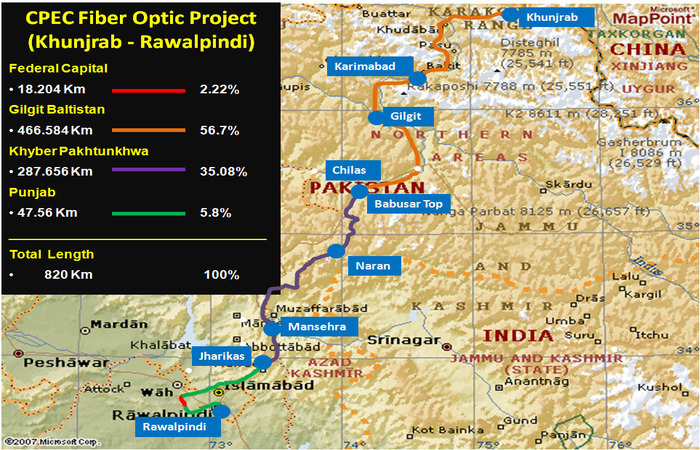
✅ Fiber optic connectivity
✅ Universities and vocational training cente
The population of the city has risen to approximately 100,000 as analysis of 2016.

Gwadar is the district headquarters of Gwadar District and the tehsil (subdistrict) headquarters of Gwadar Tehsil, which is administratively subdivided into five Union councils. Three of these councils, the northern, central, and southern councils, form Gwadar city.
Gwadar’s location and history have given it a unique blend of cultures. The Arabic influence upon Gwadar is strong as a consequence of the Omani era and its close proximity to the Arabian peninsula. The legacy of the Omanis is observed in the local Makrani population who can trace their lineage to Arabs and Zanjs slaves, who settled in the town during Omani rule. They have an Arab dance and music called Liwa, which is also performed in the Arabian peninsula.

Gwadar Port serves as a strategic asset for China, offering a potential listening post to monitor Indian naval activities in the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Aden.
The port’s location is crucial for Central Asia and South Asia, including the Caspian Region, Central Asian Republics, Afghanistan, and Iran. This region, rich in energy resources, holds immense economic potential and geopolitical significance on the global stage.
Additionally, Iran has expressed support for the development of Gwadar and its port, further solidifying its regional importance.
Historically, Gwadar’s economy relied primarily on fishing. However, it is now undergoing rapid development, transforming from a small fishing village into a major port city with modern infrastructure.
Key milestones in Gwadar’s economic transformation:
On June 20, 2016, construction began on a $2 billion, 10-square-kilometer tax-exempt industrial zone in Gwadar.
Key Features:
✅ Tax-free industrial hub
✅ 300 MW power plant dedicated to the industrial zone
✅ Boost for trade and investment
